5G Indoor Base Station Antenna
Problem Description
Design Challenges
The design and implementation of the 5G indoor base station antenna is very challenging mainly due to the following reasons:
- Integration of the normal 2G, 3G and 4G antenna specifications with modern 5G antenna specifications for quad-band multi-antenna system performance.
- Four frequency bands are considered to meet return loss and directivity requirements.
- Large fractional bandwidth requirement in the new sub-6 GHz spectrum covering the frequency bands, 3.3 GHz to 3.8 GHz and 4.8 GHz to 5.0 GHz.
- Compact, light-weight, low profile, and low maintenance with a simple feeding structure.
- Stable radiation patterns within the desired frequency bands and high polarization purity (dual-polarization desired).
AI-driven Design with SADEA-IV
Optimization Problem
For the given 5G base station antenna structure, the specifications set as the optimization goals are as follows:
- Maximum reflection coefficient (S11) < -10 dB (0.69 GHz to 0.96 GHz)
- Maximum reflection coefficient (S11) < -10 dB (1.71 GHz to 2.7 GHz)
- Maximum reflection coefficient (S11) < -10 dB (3.3 GHz to 3.8 GHz)
- Maximum reflection coefficient (S11) < -10 dB (4.8 GHz to 5.0 GHz)
- Minimum directivity (D) > 2 dBi (0.69 GHz to 0.96 GHz)
- Minimum directivity (D) > 2 dBi (1.71 GHz to 2.7 GHz)
- Minimum directivity (D) > 2 dBi (3.3 GHz to 3.8 GHz)
- Minimum directivity (D) > 2 dBi (4.8 GHz to 5.0 GHz)
- Number of resonances (NR) > 1 (0.69 GHz to 0.96 GHz)
- Number of resonances (NR) > 1 (1.71 GHz to 2.7 GHz)
- Number of resonances (NR) > 1 (3.3 GHz to 3.8 GHz)
- Number of resonances (NR) > 1 (4.8 GHz to 5.0 GHz)
- Note that resonances are only required in the antenna’s operating bands when the returning loss is poor and return loss matching might be needed. Hence, if the return loss specification is met in any of the bands, it is assumed that a resonance exists and NR is defaulted to 1.
Layout of the 5G Indoor Base Station Antenna
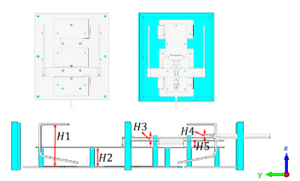
(a) The geometry of the 5G Indoor Base Station Antenna.
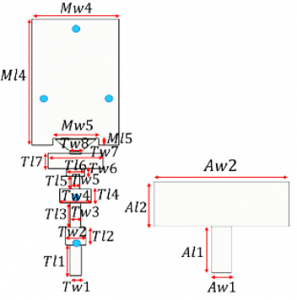
(b) The first and second layers of the 5G Indoor Base Station Antenna.

(c) The third and fourth layers of the 5G Indoor Base Station Antenna.
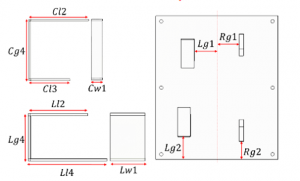
(d) The metal strips and reflector base of the 5G Indoor Base Station Antenna.
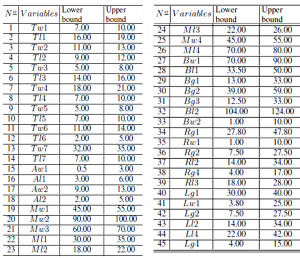
Search Ranges of the Design Parameters
Synthesis and Measurement Results
The design obtained by the latest SADEA (in-house at the moment) is verified through a physical implementation.
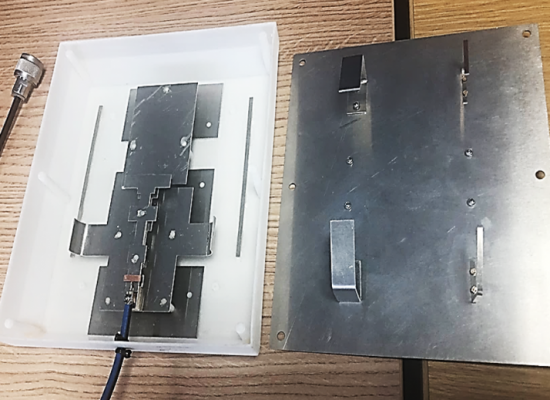


For this case:
- The synthesized antenna by the latest SADEA-IV obtains the following results using 599 EM simulations in 5.5 days.
- Maximum reflection coefficient (S11) = -10.64 dB (0.69 GHz to 0.79 GHz)
- Maximum reflection coefficient (S11) = -10.03 dB (1.71 GHz to 2.7 GHz)
- Maximum reflection coefficient (S11) = -10.81 dB (3.3 GHz to 3.8 GHz)
- Maximum reflection coefficient (S11) = -11.51 dB (4.8 GHz to 5.0 GHz)
- Maximum reflection coefficient (S11) = -13.58 dB (4.8 GHz to 5.0 GHz)
- Minimum directivity (D) = 5.88 dBi (0.69 GHz to 0.79 GHz)
- Minimum directivity (D) = 6.57 dBi (1.71 GHz to 2.7 GHz)
- Minimum directivity (D) = 7.80 dBi (3.3 GHz to 3.8 GHz)
- Minimum directivity (D) = 6.04 dBi (4.8 GHz to 5.0 GHz)
- The measurement results are in close agreement with the simulation results.
- The size of the fabricated antenna is 170.6 mm x 200 mm x 37 mm.